Note
PAD
- Consider ABI if not already completed
- Lifestyle modification: diet, exercise
- Encourage ≥ 30-45 mins of exercise at least 3 days/wk
- Tobacco cessation therapies: behavioral, pharmacologic
- BP control
- Preference for ACEi
- Cholesterol control: statin +/- ezetimibe and/or PCSK9i
- for LDL-C/Lp(a) lowering
- DM control (if indicated)
- Consider SGLT2i, GLP-1
- Exercise therapy, Supervised exercise training
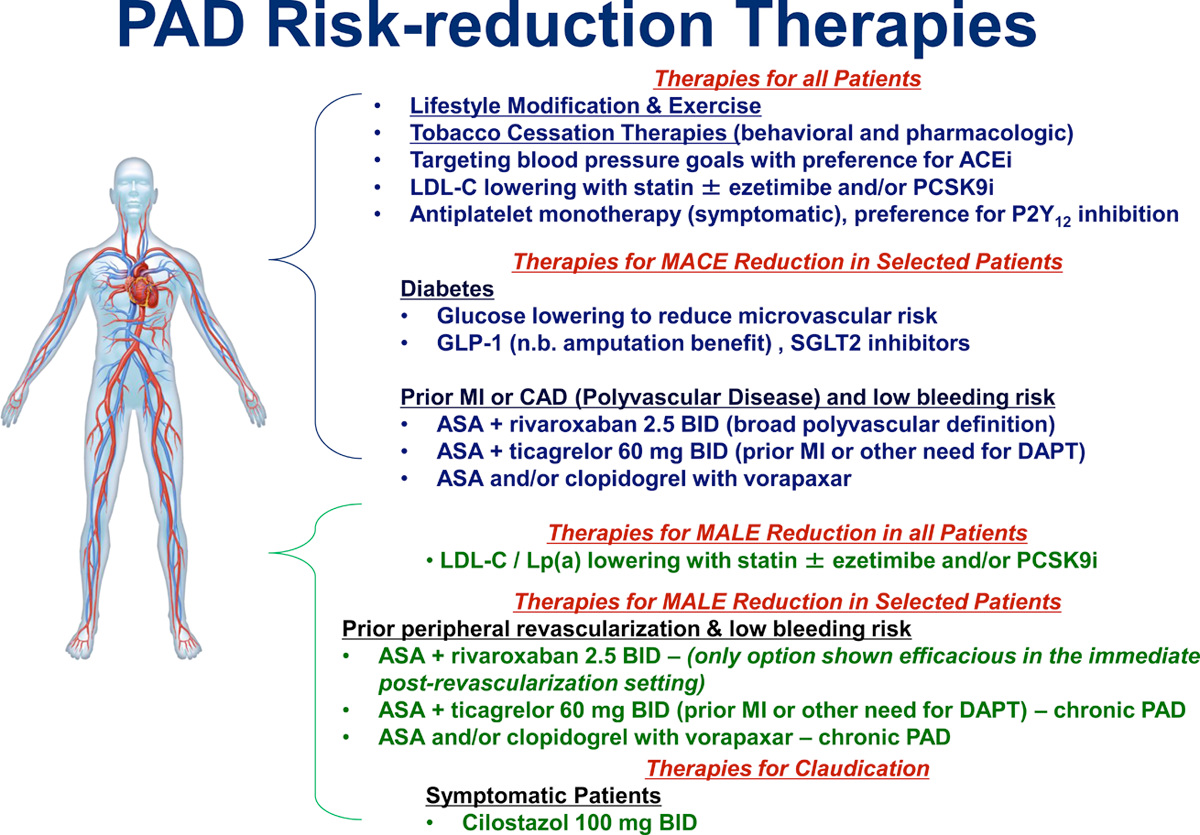
- Antiplatelet therapy
- Options:
- ASA or clopidogrel monotherapy
- if prior PI/CAD and *low* bleeding risk:
- ASA + rivaroxaban 2.5 mg BID
- ASA + ticagrelor 60 mg BID (prior MI or other need for DAPT)
- ASA and/or clopidogrel with vorapaxar
- if prior peripheral revascularization and *low* bleeding risk
- ASA + rivaroxaban 2.5 mg BID (only option shown efficacious in immediate post-revasc setting)
- ASA + ticagrelor 60 mg BID (prior MI or other need for DAPT) - chronic PAD
- ASA and/or clopidogrelwith vorapaxar - chronic PAD
- If claudication, cilostazol 100 mg BID
- avoid if pt has NYHA Class 3 or 4 HF d/t ↑ mortality w/ PDE inhibitors in these pts
History
- History: pain relieved w/ sitting down or standing still
- By contrast, in pts with spinal stenosis, pain is only by sitting down (i.e. Sx persist even if standing still)
- does not cause nocturnal leg cramps (neither does lumbar stenosis)
- Intermittent claudication
- supervised exercise program is part of the initial Tx regiman in all pts w/ intermittent claudication
Diagnosis
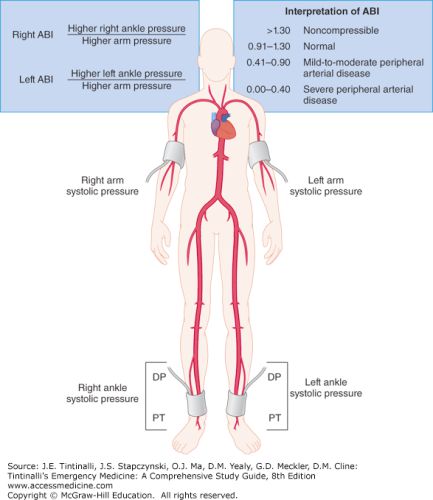
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) interpretation:
- normal ABI: 0.91-1.30
- mild-to-moderate PAD: 0.41-0.90
- severe PAD: 0.00-0.40
- Duplex (ultrasound + Doppler) waveform interpretation in PVD:
- normal → TRIphasic
- moderate occlusion → BIphasic
- severe occlusion → MONOphasic
Management
- Encourage ≥ 30-45 mins of exercise at least 3 days/wk
- ⚠️ Avoid cilostazol for Tx of PAD in pts w/ NYHA Class 3 or 4 HF
- d/t ↑ mortality w/ PDE inhibitors in these pts
- Patients with symptomatic PAD (claudication with ABI < 0.85, or previous revascularization or amputation) are considered a ‘high-risk’ ASCVD group and are recommended to be on high-intensity statin (See Chapter 61)
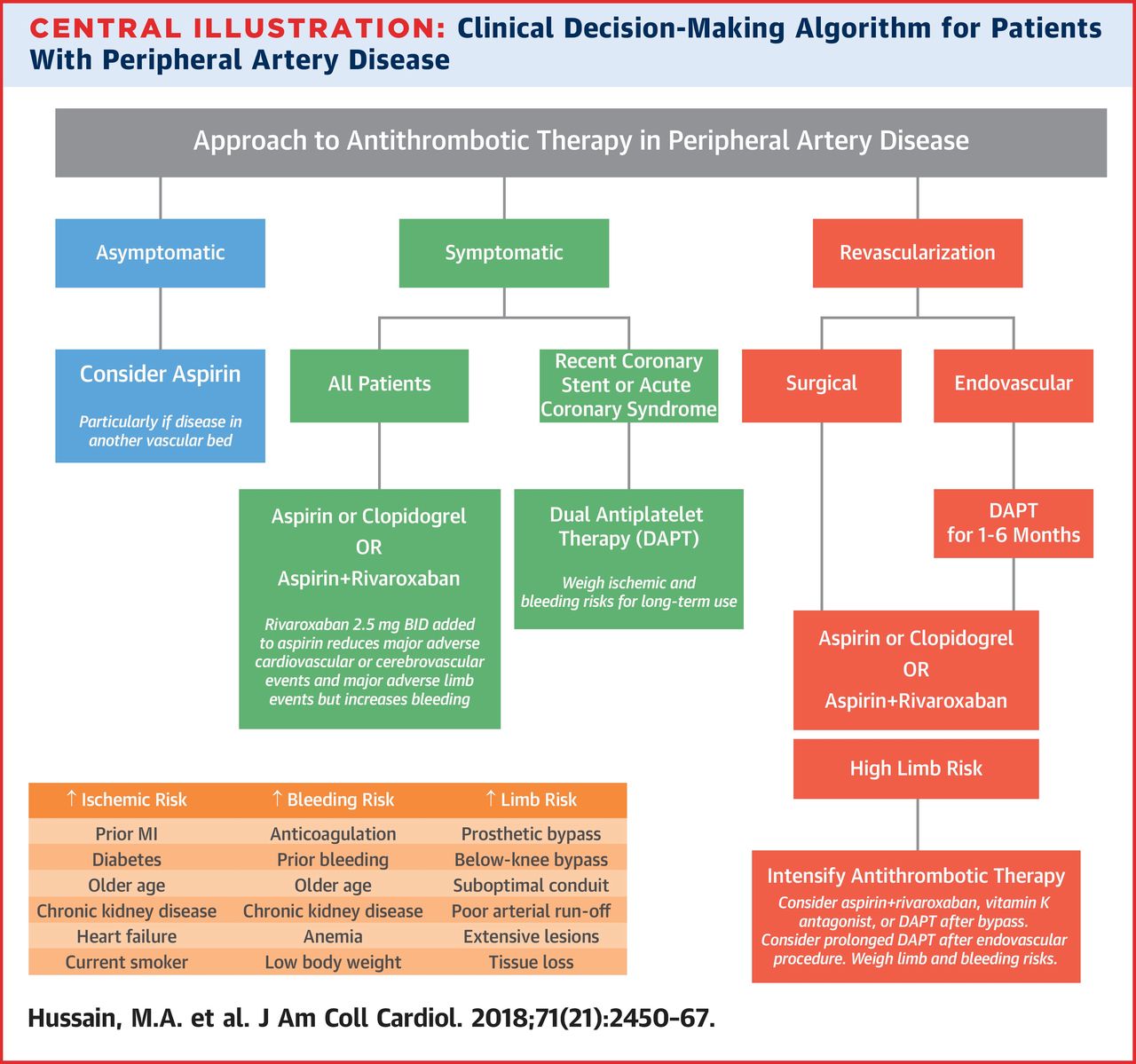
- Anti-thrombotic therapy (Hussain et al. 2018)
- Asymptomatic:
- AHA/ACC PAD guideline recommends antiplatelet therapy as reasonable if ABI ≤ 0.90
- European Society of Cardiology guideline recommends against routine antiplatelet therapy in asymptomatic pts
- Symptomatic
- Tx w/ antithrombotic - monotherapy with either ASA or clopidogrel
- s/p revascularization (See Figure 37.1 and Figure 37.2)
- Indications for surgical intervention for PVD:
- rest pain
- intractable claudication
- non-healing infection
- tissue necrosis
Hussain, Mohamad A., Mohammed Al-Omran, Mark A. Creager, Sonia S. Anand, Subodh Verma, and Deepak L. Bhatt. 2018.
“Antithrombotic Therapy for Peripheral Artery Disease.” Journal of the American College of Cardiology 71 (21): 2450–67.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.03.483.